入门指南
在线尝试 Riverpod
要尝试 Riverpod,请在 Dartpad 或 Zapp 上在线试用:
安装包
知道要安装哪个包后,请继续在一行中将依赖项添加到应用,如下所示:
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
flutter pub add flutter_riverpod
flutter pub add dev:custom_lint
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_lint
flutter pub add hooks_riverpod
flutter pub add flutter_hooks
flutter pub add dev:custom_lint
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_lint
flutter pub add flutter_riverpod
flutter pub add riverpod_annotation
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_generator
flutter pub add dev:build_runner
flutter pub add dev:custom_lint
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_lint
flutter pub add hooks_riverpod
flutter pub add flutter_hooks
flutter pub add riverpod_annotation
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_generator
flutter pub add dev:build_runner
flutter pub add dev:custom_lint
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_lint
- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
dart pub add riverpod
dart pub add dev:custom_lint
dart pub add dev:riverpod_lint
dart pub add riverpod
dart pub add riverpod_annotation
dart pub add dev:riverpod_generator
dart pub add dev:build_runner
dart pub add dev:custom_lint
dart pub add dev:riverpod_lint
或者,您可以从以下 pubspec.yaml 位置手动将依赖项添加到您的应用:
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_riverpod: ^3.3.0
dev_dependencies:
custom_lint:
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
hooks_riverpod: ^3.3.0
flutter_hooks:
dev_dependencies:
custom_lint:
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_riverpod: ^3.3.0
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
custom_lint:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
hooks_riverpod: ^3.3.0
flutter_hooks:
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
custom_lint:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
然后,使用 flutter pub get 安装包。
dart run build_runner watch.- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
dependencies:
riverpod: ^3.2.1
dev_dependencies:
custom_lint:
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
dependencies:
riverpod: ^3.2.1
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
custom_lint:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
riverpod_lint: ^undefined
然后,使用 dart pub get 安装包。
dart run build_runner watch.就是这样。你已将 Riverpod 添加到你的应用中!
启用 riverpod_lint/custom_lint
Riverpod 附带一个可选的 riverpod_lint 包, 该包提供 lint 规则以帮助您编写更好的代码, 并提供自定义重构选项。
如果按照前面的步骤操作,则应该已经安装了该包, 但需要单独的步骤才能启用它。
要启用riverpod_lint,您需要在 pubspec.yaml 文件的旁边添加一个
analysis_options.yaml 文件,并包含以下内容:
analyzer:
plugins:
- custom_lint
现在,如果在代码库中使用 Riverpod 时出错,您应该会在 IDE 中看到警告。
要查看警告和重构的完整列表,请前往 riverpod_lint 页面。
这些警告不会显示在 dart analyze 命令的结果中。
如果要在 CI 或终端中检查这些警告,可以运行以下命令:
dart run custom_lint
使用示例:Hello world
现在我们已经安装了 Riverpod,我们可以开始使用它了。
以下代码片段展示了如何使用我们的新依赖项来创建 “Hello world”:
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_riverpod/flutter_riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
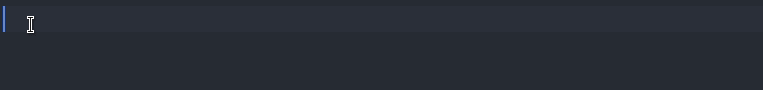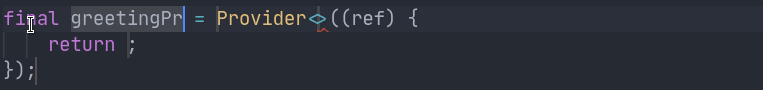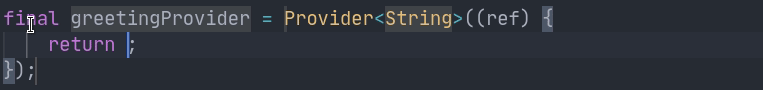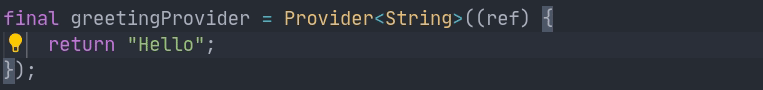
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend ConsumerWidget instead of StatelessWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends ConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text(value),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_hooks/flutter_hooks.dart';
import 'package:hooks_riverpod/hooks_riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend HookConsumerWidget instead of HookWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends HookConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// We can use hooks inside HookConsumerWidget
final counter = useState(0);
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text('$value ${counter.value}'),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_riverpod/flutter_riverpod.dart';
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend ConsumerWidget instead of StatelessWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends ConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text(value),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_hooks/flutter_hooks.dart';
import 'package:hooks_riverpod/hooks_riverpod.dart';
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend HookConsumerWidget instead of HookWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends HookConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// We can use hooks inside HookConsumerWidget
final counter = useState(0);
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text('$value ${counter.value}'),
),
),
);
}
}
然后,使用 flutter run 启动应用程序。
这将在您的设备上呈现 “Hello world”。
- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
import 'package:riverpod/riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
// This object is where the state of our providers will be stored.
final container = ProviderContainer();
// Thanks to "container", we can read our provider.
final value = container.read(helloWorldProvider);
print(value); // Hello world
}
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
// This object is where the state of our providers will be stored.
final container = ProviderContainer();
// Thanks to "container", we can read our provider.
final value = container.read(helloWorldProvider);
print(value); // Hello world
}
然后,使用 dart lib/main.dart 启动应用程序。
这将在控制台中打印 “Hello world”。
更进一步:安装代码片段
如果你使用的 Flutter 是 VS Code ,请考虑使用 Flutter Riverpod Snippets
如果您使用的 Flutter 是 Android Studio 或 IntelliJ ,请考虑使用 Flutter Riverpod Snippets
选择你的下一步
了解一些基本概念:
跟着教程走: