Getting started
Try Riverpod online
To get a feel of Riverpod, try it online on Dartpad or on Zapp:
Installing the package
Riverpod comes as a main "riverpod" package that’s self-sufficient, complemented by optional packages for using code generation (About code generation) and hooks (About hooks).
For the sake of being compatible with the latest json_serializable package, some Riverpod packages are currently only compatible with Flutter's beta channel or later.
If pub get is failing due to version solving issues, consider switching to the beta channel by running:
flutter channel beta
Or consider downgrading Riverpod to <=3.1.0.
Once you know what package(s) you want to install, proceed to add the dependency to your app in a single line like this:
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
flutter pub add flutter_riverpod
flutter pub add hooks_riverpod
flutter pub add flutter_hooks
flutter pub add flutter_riverpod
flutter pub add riverpod_annotation
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_generator
flutter pub add dev:build_runner
flutter pub add hooks_riverpod
flutter pub add flutter_hooks
flutter pub add riverpod_annotation
flutter pub add dev:riverpod_generator
flutter pub add dev:build_runner
- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
dart pub add riverpod
dart pub add riverpod
dart pub add riverpod_annotation
dart pub add dev:riverpod_generator
dart pub add dev:build_runner
Alternatively, you can manually add the dependency to your app from within your pubspec.yaml:
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_riverpod: ^3.2.1
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
hooks_riverpod: ^3.2.1
flutter_hooks:
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_riverpod: ^3.2.1
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
flutter: ">=3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
hooks_riverpod: ^3.2.1
flutter_hooks:
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
Then, install packages with flutter pub get.
- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
dependencies:
riverpod: ^3.2.1
name: my_app_name
environment:
sdk: ^3.7.0
dependencies:
riverpod: ^3.2.1
riverpod_annotation: ^4.0.2
dev_dependencies:
build_runner:
riverpod_generator: ^4.0.3
Then, install packages with dart pub get.
If using code-generation, you can now run the code-generator with:
dart run build_runner watch -d
That's it. You've added Riverpod to your app!
Enabling riverpod_lint
Riverpod comes with an optional riverpod_lint package that provides lint rules to help you write better code, and provide custom refactoring options.
Riverpod_lint is implemented using analysis_server_plugin. As such, it is installed through analysis_options.yaml
Long story short, create an analysis_options.yaml next to your pubspec.yaml and add:
plugins:
riverpod_lint: <latest version from https://pub.dev/packages/riverpod_lint>
You should now see warnings in your IDE if you made mistakes when using Riverpod in your codebase.
To see the full list of warnings and refactorings, head to the riverpod_lint page.
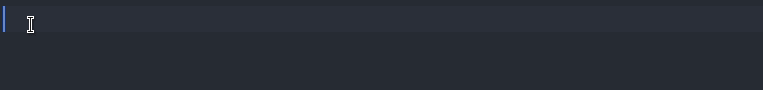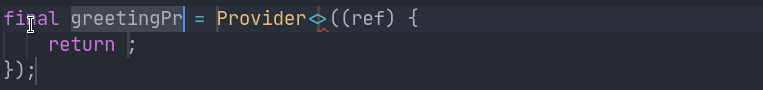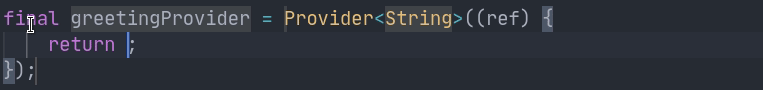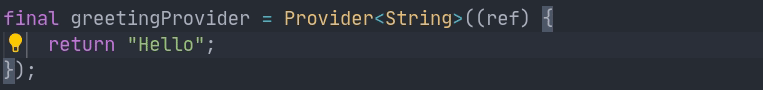
Usage example: Hello world
Now that we have installed Riverpod, we can start using it.
The following snippets showcase how to use our new dependency to make a "Hello world":
- Flutter
- Dart only
- riverpod
- riverpod + flutter_hooks
- riverpod_generator
- riverpod_generator + flutter_hooks
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_riverpod/flutter_riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend ConsumerWidget instead of StatelessWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends ConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text(value),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_hooks/flutter_hooks.dart';
import 'package:hooks_riverpod/hooks_riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend HookConsumerWidget instead of HookWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends HookConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// We can use hooks inside HookConsumerWidget
final counter = useState(0);
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text('$value ${counter.value}'),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_riverpod/flutter_riverpod.dart';
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend ConsumerWidget instead of StatelessWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends ConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text(value),
),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_hooks/flutter_hooks.dart';
import 'package:hooks_riverpod/hooks_riverpod.dart';
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
runApp(
// For widgets to be able to read providers, we need to wrap the entire
// application in a "ProviderScope" widget.
// This is where the state of our providers will be stored.
ProviderScope(
child: MyApp(),
),
);
}
// Extend HookConsumerWidget instead of HookWidget, which is exposed by Riverpod
class MyApp extends HookConsumerWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// We can use hooks inside HookConsumerWidget
final counter = useState(0);
final String value = ref.watch(helloWorldProvider);
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Example')),
body: Center(
child: Text('$value ${counter.value}'),
),
),
);
}
}
Then, start the application with flutter run.
This will render "Hello world" on your device.
- riverpod
- riverpod_generator
import 'package:riverpod/riverpod.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
final helloWorldProvider = Provider((_) => 'Hello world');
void main() {
// This object is where the state of our providers will be stored.
final container = ProviderContainer();
// Thanks to "container", we can read our provider.
final value = container.read(helloWorldProvider);
print(value); // Hello world
}
import 'package:riverpod_annotation/riverpod_annotation.dart';
part 'main.g.dart';
// We create a "provider", which will store a value (here "Hello world").
// By using a provider, this allows us to mock/override the value exposed.
String helloWorld(Ref ref) {
return 'Hello world';
}
void main() {
// This object is where the state of our providers will be stored.
final container = ProviderContainer();
// Thanks to "container", we can read our provider.
final value = container.read(helloWorldProvider);
print(value); // Hello world
}
Then, start the application with dart lib/main.dart.
This will print "Hello world" in the console.
Going further: Installing code snippets
If you are using Flutter and VS Code , consider using Flutter Riverpod Snippets
If you are using Flutter and Android Studio or IntelliJ, consider using Flutter Riverpod Snippets